Sternoclavicular Dislocation
- Traumatic injury resulting in either anterior or posterior dislocation of the medial clavicle in relation to the sternum
- Usually due to a force on the shoulder with an abducted arm
- Anterior dislocation is usually treated nonoperatively
- Posterior dislocation is more serious because the trachea, esophagus, thoracic duct, and large vessels in the mediastinum may be damaged by the displaced end of the clavicle
- Mechanism
- Motor vehicle accident most common
- Sports injury also common
- Direct blow (e.g. another athlete falls on the SC joint)
- Usually results in posterior dislocation
- Indirect force (i.e. blow to the shoulder while unable to change position)
- May be anterior or posterior
- Timing of injury
- Acute vs. chronic - has implications on disposition and management
- Other locations of pain
- Associated symptoms
- Posterior dislocations can compress mediastinal structures
- Paresthesias in the arm (neural impingement)
- Venous congestion
- Dyspnea
- Dysphagia
- Tachypnea
- Stridor
- Hand dominance (right vs. left hand dominant)
- Profession
- Anticoagulation
- Last dose?
- Last time the patient ate (NPO status)
Vitals
- Key to assess upon initial presentation especially if associated symptoms are present (dyspnea, dysphagia, etc.) as critical structures may be compromised
- Key to assess upon initial presentation especially if associated symptoms are present (dyspnea, dysphagia, etc.) as critical structures may be compromised
- Deformity - anterior dislocation can lead to a palpable bump
- Usually painful over the SC joint
Motor Exam:
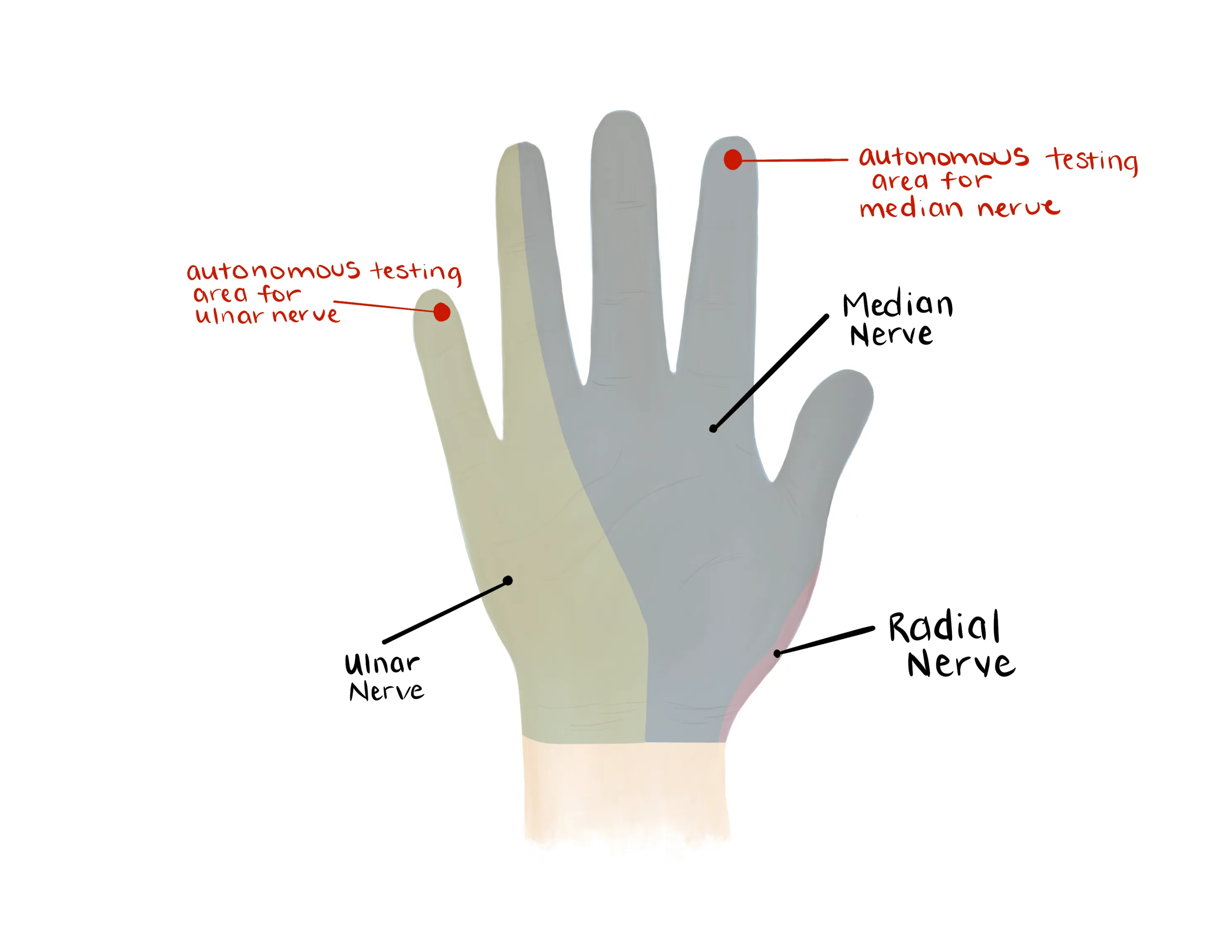
- Median Nerve/ Anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)
- Flexion of wrist, fingers, thumb
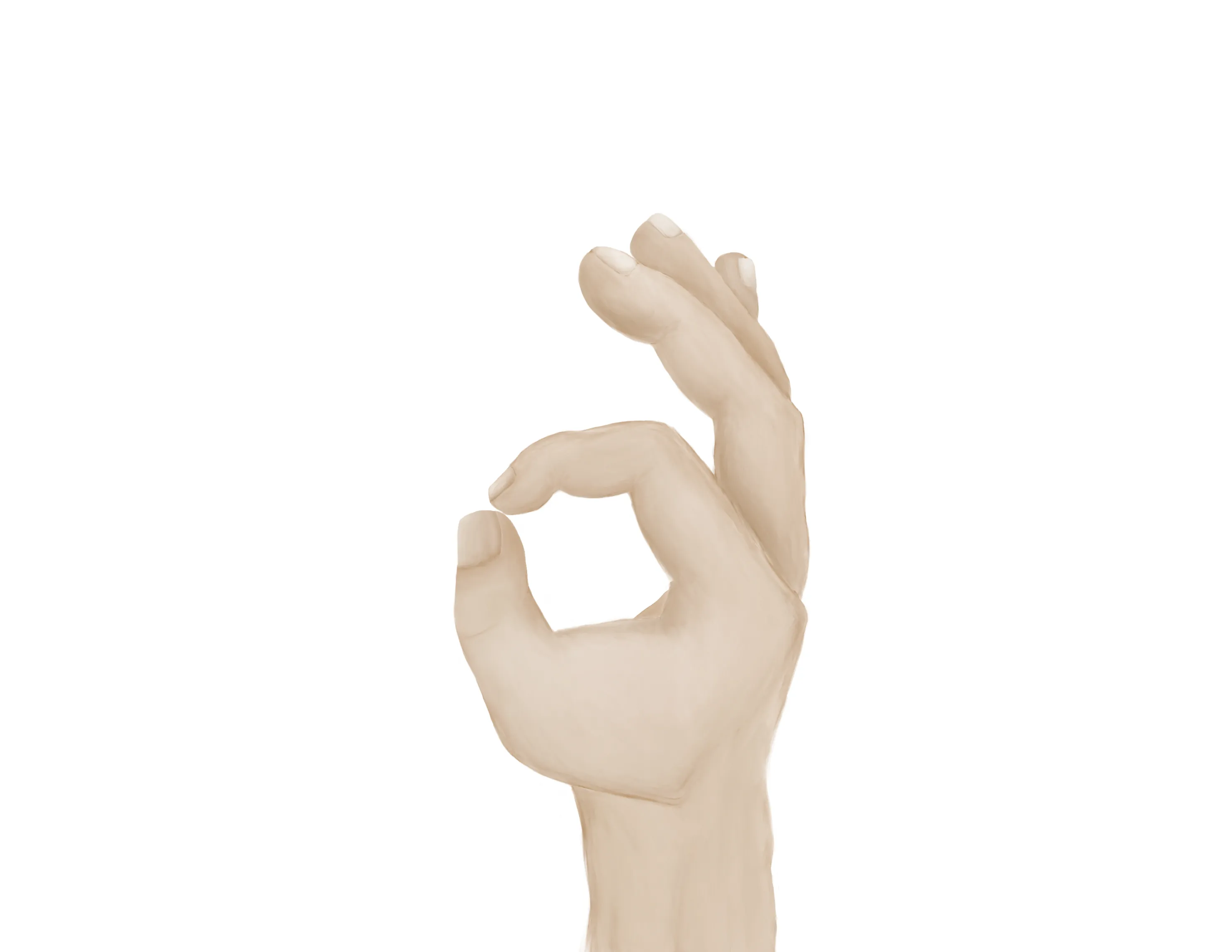
- “A-OK sign” = AIN
- Tests flexion of thumb IP joint (FPL) and flexion of index DIP joint (FDP)
- Radial nerve/ Posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)
-
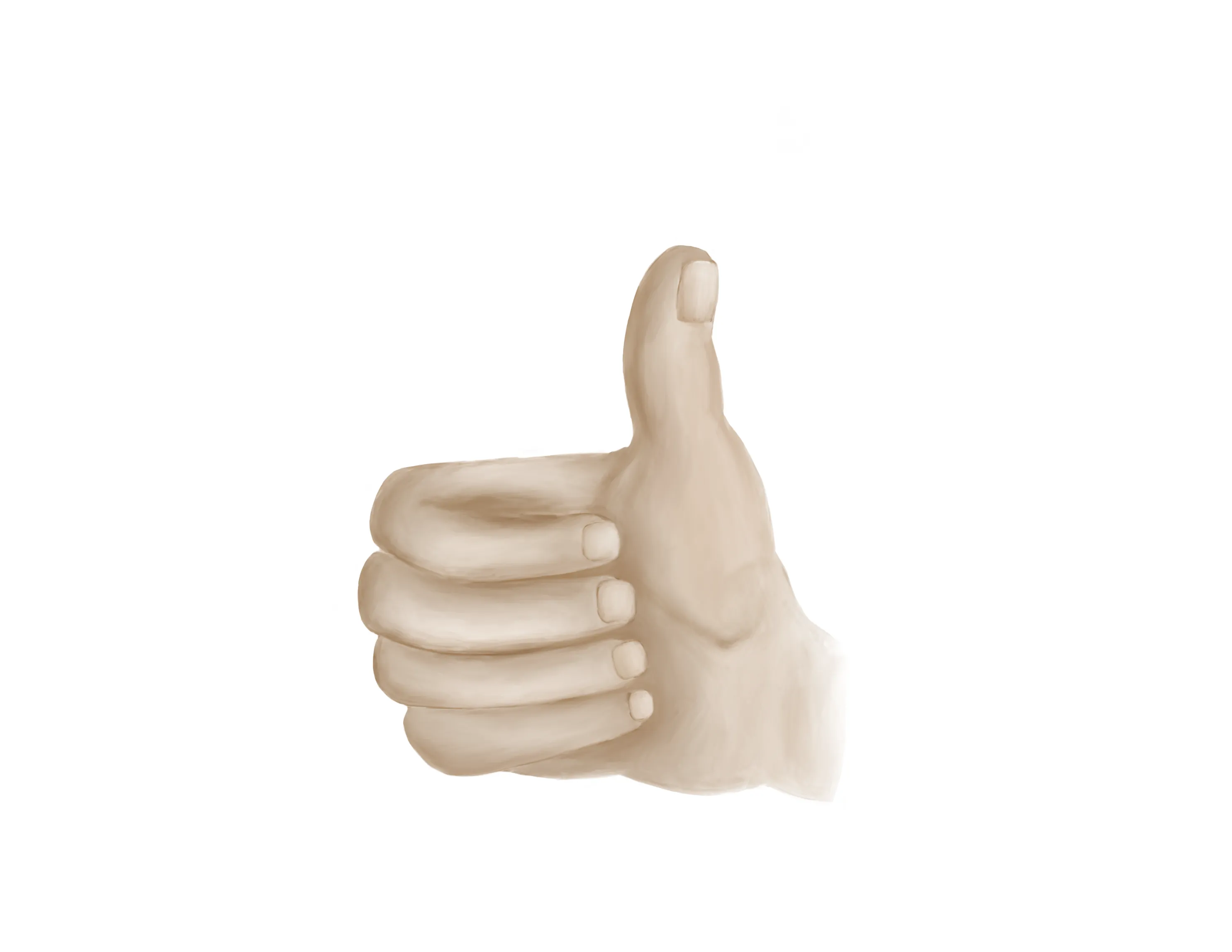

- Extension of wrist, fingers, thumb
- “Thumbs up” = PIN
- Tests extension of thumb IP and MCP joints (EPL))
- Palm on flat surface and lifting/extending thumb off the surface is also a good test for PIN (tests extension of thumb MCP joint (EPL))
- Ulnar nerve
- Median, Radial, Ulnar nerve distributions
- Radial artery, Ulnar artery
- If having difficulty with palpation radial artery, use a doppler
- Capillary refill to digits
- Venous congestion in the ipsilateral extremity?
- Exam may improve by turning head to the affected side
- Assess ROM at the neck, shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand (may be pain limited)
- AP of the clavicle, AP/Serendipity view of the SC joints
- Serendipity view - better for assessing anterior or posterior dislocation
- CT scan - study of choice
- Confirmatory test if there is doubt about direction of dislocation
- Can also view the mediastinal structures if concerned about compression due to posterior dislocation
- MRI - rarely needed
- Can differentiate physeal injuries in children
- Leave to discretion of the orthopaedic team
Medical Decision Making
Chronic dislocation or atraumatic subluxation:
*** is a *** y/o ***R/L hand-dominant individual with a history of *** presenting with ***, found to have an ***chronic SC dislocation/subluxation. The patient reported a trauma to the shoulder ***time. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with no poke holes or punctate wounds. There are no signs of venous congestion or neural injury. Imaging reveals ***. Given that the inciting injury occured >3 weeks ago with evolution of the symptoms, this appears to be a chronic process. The patient was immobilized in a sling and will follow up with orthopaedics surgery in 7-10 days.
Acute dislocation (anterior or posterior):
*** is a *** y/o ***R/L hand-dominant individual with a history of *** presenting with an injury to the *** shoulder which occurred while ***, found to have an posterior/anterior*** SC dislocation. On exam, the patient is/is not*** neurovascularly intact with vitals within normal limits. The patient denies/endorses*** dysphagia, dyspnea, and paresthesias. Orthopaedics was consulted and the patient was kept NPO. Orthopaedics to provide further recommendations.
Acute dislocation with signs of mediastinal compression :
- Consult orthopaedic surgery immediately
- Consult thoracic surgery immediately
- NPO, preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- Consult orthopaedic surgery
- NPO, preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- WB status: Nonweightbearing for comfort
- Diet: Regular
- Analgesia: short course of narcotic pain medication, tylenol (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 25 pills
- Immobilization
- Sling immobilization for comfort
- Disposition: Home with follow up in orthopedic surgery clinic in 1 week
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S43.2 | Subluxation and dislocation of sternoclavicular joint |
| S43.21 | Anterior subluxation and dislocation of sternoclavicular joint |
| S43.22 | Posterior subluxation and dislocation of sternoclavicular joint |
| S23.420 | Sprain of sternoclavicular (joint) (ligament) |