Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) Injuries
- Stability of the metatarsophalangeal joints of the toes is supported by a joint capsule with a thick plantar plate in addition to ligamentous and musculotendinous structures
-
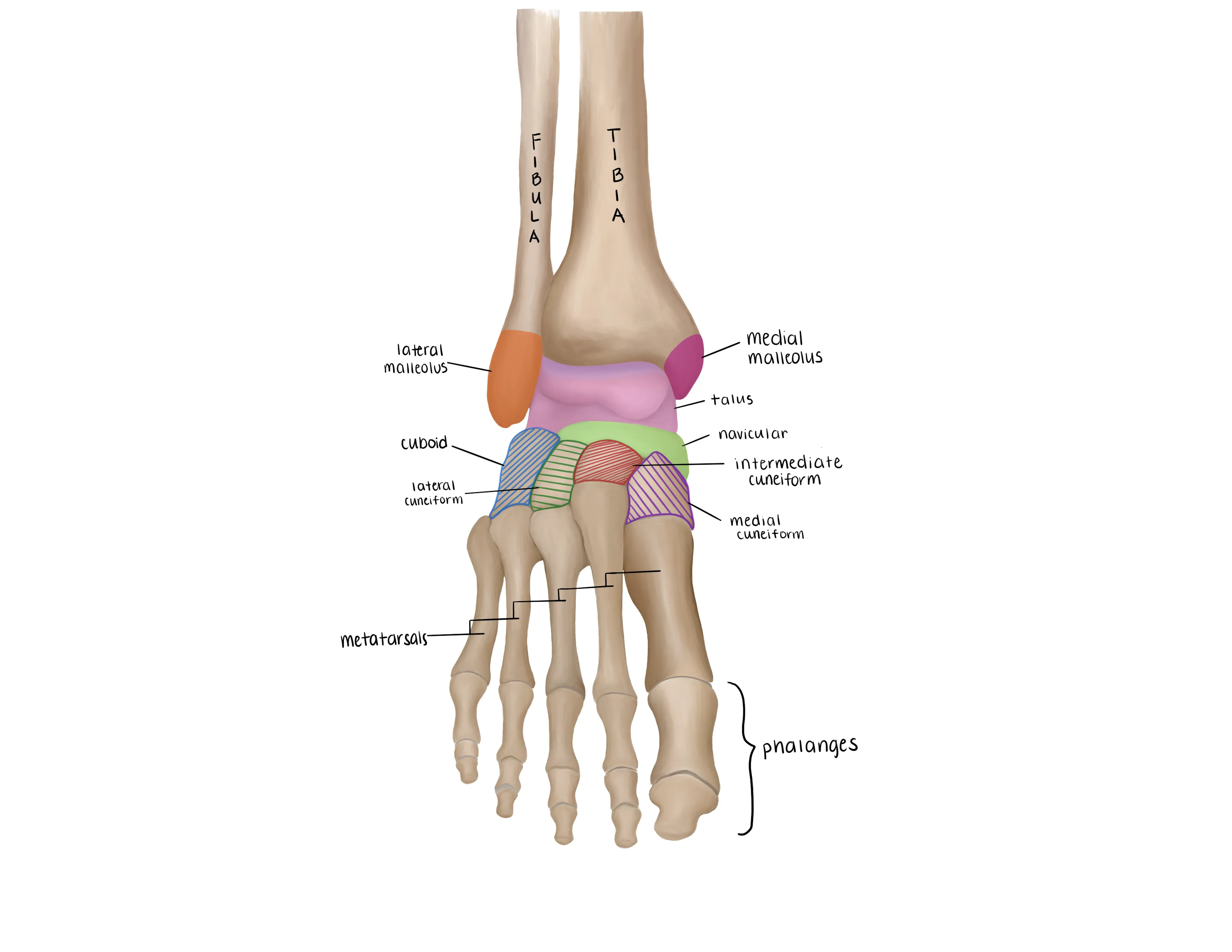
- Sesamoid bones are embedded in the plantar structures of the 1st MTP joint
- “Turf toe” is a hyperextension sprain of the 1st MTP joint
- Dislocations should be promptly reduced
- Osteoarthritis and gout are common causes of atraumatic pain at the MTP joints
- Fractures of the talus account for 5-7% of foot injuries
- Classified anatomically by the location of the fracture
- Mechanism
- Turf toe
- Hyperextension of the MTP joint
- Stretches plantar capsule and plate
- Dislocation of the 1st MTP joint
- High-energy trauma such as a motor vehicle accident
- Dislocation of 2nd-5th MTP joints
- Low-energy trauma such as stubbing the toe
- Timing of injury
- Dislocations that are not promptly reduced can lead to degenerative changes, chronic pain, and stiffness
- Delayed treatment of turf toe can lead to further injury and increased time necessary for healing
- Risk factors
- Sprinting/cutting sports (e.g. football, soccer)
- Artificial turf
- Ballet
- Tobacco use
- Poor healing potential
- Comorbidities
- MTP osteoarthritis
- May be exacerbated by minor trauma
Vitals
- Swelling and ecchymosis at the involved MTP joint
- Deformity associated with dislocation
- Usually dislocated dorsally
- Dorsal prominence and shortening of toe
- Tenderness at the MTP joint
- Palpate medial and lateral collateral ligaments, dorsal capsule, and plantar capsule
Motor Exam:
- EHL/FHL - Extension/Flexion of the great toe (often painful)
- Flexion and extension of the involved toe (often painful)
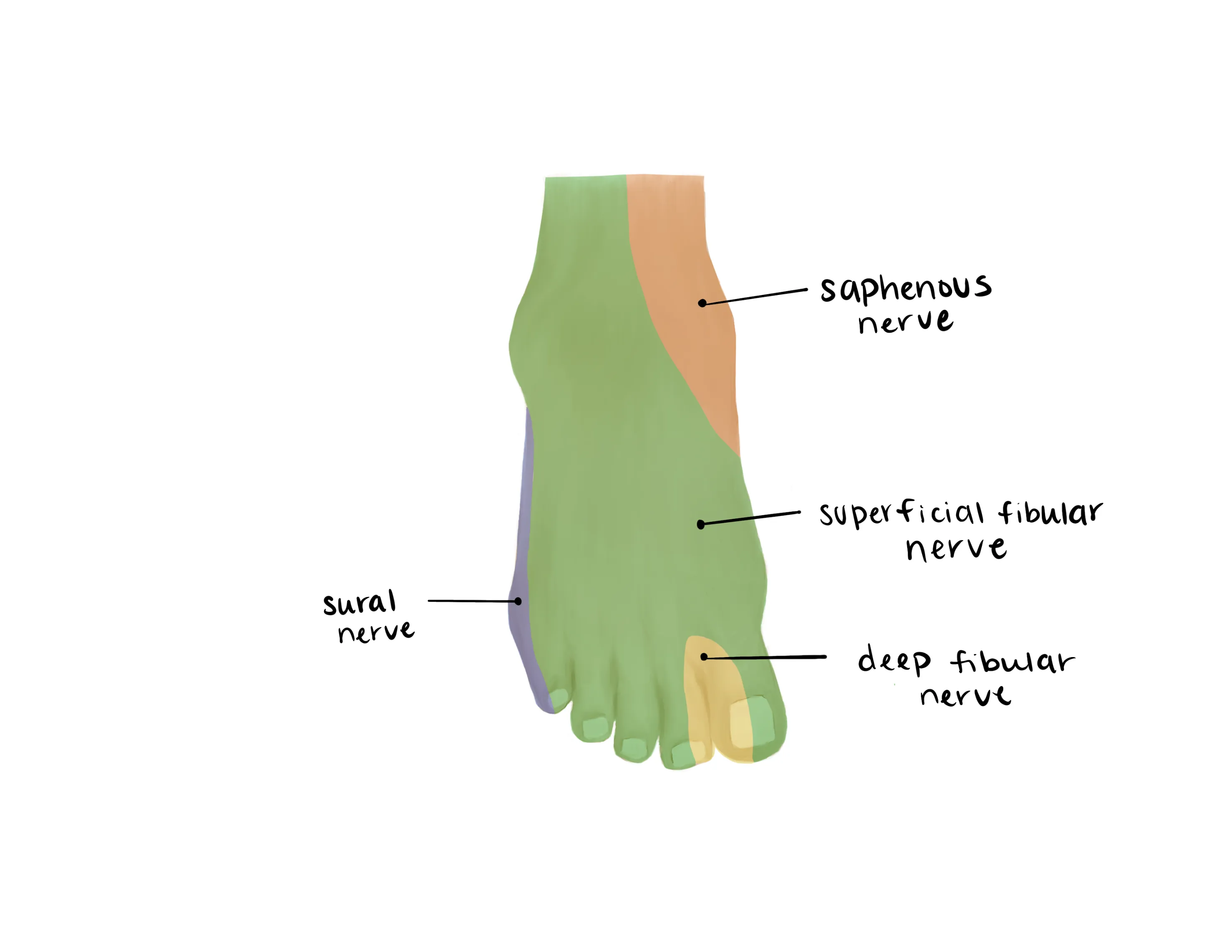
- Sural (Lateral)
- Saphenous(medial)
- Superficial Peroneal(dorsum)
- Deep Peroneal (1st web space)
- Tibial (plantar)
-
- Capillary refill to involved toe
- Decreased motion secondary to pain
- Turf toe
- Increased pain with passive extension
- Radiographs AP/lateral/oblique of involved foot
- Dislocation readily identified
- Avulsion fracture at base of proximal phalanx suggests capsular injury
- Joint space narrowing, osteophytosis, sclerosis suggest chronic etiology (typically osteoarthritis)
- MRI - not necessary in the ED
- CT scan - not necessary in the ED
- May be obtained to evaluate intra-articular fractures
Medical Decision Making
Turf Toe
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an injury to the ***R/L great toe and concern for a turf toe injury after hyperextension of the MTP joint. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact. There is pain at the base of the great toe and tenderness with palpation of the dorsal MTP joint. The injury is closed and isolated. Radiographs reveal ***. The patient was placed into a rigid-soled postop shoe. The patient was permitted to bear weight as tolerated, but instructed to avoid strenuous activity on the injured foot. The patient will ice and elevate the toe as needed and follow up with their primary care physician if the symptoms were to worsen.
Closed Toe Dislocation
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an injury to the ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th toe and concern for a dislocation of the MTP joint after mechanism***. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact. There is gross deformity with dorsal prominence and shortening of the toe. There is pain at the MTP joint. The injury is closed and isolated. Radiographs reveal ***. A closed reduction was performed. The toe was buddy-taped to the adjacent toe and the patient was placed into a rigid-soled postop shoe. The patient was permitted to bear weight as tolerated, but instructed to avoid strenuous activity on the injured foot. The patient will ice and elevate the toe as needed and follow up with orthopedic surgery for further evaluation.
Open Toe Dislocation
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an open dislocation of the ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th toe at the MTP joint after mechanism***. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with a laceration on the *** aspect of the toe that probes to fracture. The patient was given an immediate dose of IV ancef/gentamicin*** and the open wound was washed out copiously at bedside. The patient was kept NPO and orthopaedics was consulted. The patient last ate at ***.
Toe sprain, including turf toe:
- Activity Status: Bear weight as tolerated; no sports or strenuous activity
- Diet: Regular
- Analgesia: short course of narcotic pain medication, tylenol (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Rigid-sole postop shoe
- Disposition: Home with follow up with primary care clinic within 2 weeks
- Activity Status: Bear weight as tolerated; no sports or strenuous activity
- Diet: Regular
- Analgesia: short course of narcotic pain medication, tylenol (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Closed reduction, Buddy-taping, and rigid-sole postop shoe
- See reduction maneuver below
- Disposition: Home with follow up in orthopedic clinic within a week
- Consult orthopedics immediately
- NPO, preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- Ensure IV antibiotics were given (ancef, gentamicin)
- Gustillo-Anderson chart for antibiotic type and dose
- If orthopedics not immediately available, irrigate the wound thoroughly and reduce the dislocation
- WB Status: Nonweightbearing with crutches
- Diet: Regular
- Analgesia: short course of narcotic pain medication, tylenol (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Short leg splint
- Disposition: Home with follow up in orthopedic clinic within 1 week
Materials
Procedure Walkthroughs:
- Materials: Hard-soled shoe, lidocaine 1% no epi , syringe for digital block
- Prep skin at base of toe and administer digital block
- Insert needle from dorsal to plantar on the medial and lateral side of the affected toe
- Draw the plunger back before injecting lidocaine to ensure you are not in a vessel when doing so
- Inject 1% lidocaine in these space to number the digital nerves
- Pull traction in line with the deformity
- Palpable reduction of dislocation and resolution of deformity
- Obtain post-reduction x-rays to confirm successful reduction
- Apply a well-fitting rigid-soled postop shoe
- Heel pushed to the back of the shoe
- Toes approach the end of the shoe but do not hang off the edge
- Materials: Hard-soled shoe, conscious sedation team
- Have sedation team perform conscious sedation with appropriate personnel in the room
- Pull traction in line with the deformity
- Palpable reduction of dislocation and resolution of deformity
- Obtain post-reduction x-rays to confirm successful reduction
- Apply a well-fitting hard-soled rigid-soled postop shoe
- Heel pushed to the back of the shoe
- Toes approach the end of the shoe but do not hang off the edge
Procedure Notes:
PROCEDURE NOTEClosed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation
PRE-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Dislocation of ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th metatarsophalangeal dislocation
POST-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Same (refer above)
PROCEDURALIST: ***
ANESTHESIA: Digital block
NAME OF PROCEDURE: Closed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation with manipulation
PROCEDURE IN DETAIL:
The risks and benefits of the procedure were discussed at length with the patient. Risks discussed included but were not limited to post-procedural pain, numbness, and stiffness. Following informed verbal consent after discussion of risks and benefits, the patient agreed to proceed with the procedure. A timeout was performed.
Skin over the base of the toe was cleansed and prepped. A digital block was obtained with ***ml of 1% lidocaine without epinephrine. The toe was grasped and gentle traction was applied in line with the deformity. The toe was felt to relocate and deformity improved. The foot was placed into a properly fitting rigid-sole postop shoe. Radiographs were obtained which demonstrated a successful reduction without associated fractures.
After completion of the procedure, the patient’s neurovascular status was within normal limits.
NUMBER OF REDUCTION ATTEMPTS: ***
COMPLICATIONS: ***
DISPOSITION:
Discharged home weight bearing as tolerated in a hard-soled shoe with follow-up with orthopaedic surgery in 1 week.
PRE-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Dislocation of ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th metatarsophalangeal dislocation
POST-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Same (refer above)
PROCEDURALIST: ***
ANESTHESIA: Digital block
NAME OF PROCEDURE: Closed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation with manipulation
PROCEDURE IN DETAIL:
The risks and benefits of the procedure were discussed at length with the patient. Risks discussed included but were not limited to post-procedural pain, numbness, and stiffness. Following informed verbal consent after discussion of risks and benefits, the patient agreed to proceed with the procedure. A timeout was performed.
Skin over the base of the toe was cleansed and prepped. A digital block was obtained with ***ml of 1% lidocaine without epinephrine. The toe was grasped and gentle traction was applied in line with the deformity. The toe was felt to relocate and deformity improved. The foot was placed into a properly fitting rigid-sole postop shoe. Radiographs were obtained which demonstrated a successful reduction without associated fractures.
After completion of the procedure, the patient’s neurovascular status was within normal limits.
NUMBER OF REDUCTION ATTEMPTS: ***
COMPLICATIONS: ***
DISPOSITION:
Discharged home weight bearing as tolerated in a hard-soled shoe with follow-up with orthopaedic surgery in 1 week.
PROCEDURE NOTEClosed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation
PRE-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Dislocation of ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th metatarsophalangeal dislocation
POST-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Same (refer above)
PROCEDURALIST: ***
ANESTHESIA:***Conscious sedation
NAME OF PROCEDURE: Closed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation with manipulation
PROCEDURE IN DETAIL:
The risks and benefits of the procedure were discussed at length with the patient. Risks discussed included but were not limited to post-procedural pain, numbness, and stiffness. The risks of conscious sedation were also discussed with the patient. Following informed verbal consent after discussion of risks and benefits, the patient agreed to proceed with the procedure. A timeout was performed.
Conscious sedation was performed with all appropriate personnel in the room. The toe was grasped and gentle traction was applied in line with the deformity. The toe was felt to relocate and deformity improved. The foot was placed into a properly fitting rigid-sole postop shoe. Radiographs were obtained which demonstrated a successful reduction without associated fractures.
After completion of the procedure, the patient’s neurovascular status was within normal limits.
NUMBER OF REDUCTION ATTEMPTS: ***
COMPLICATIONS: ***
DISPOSITION:
Discharged home weight bearing as tolerated in a hard-soled shoe with follow-up with orthopaedic surgery in 1 week.
PRE-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Dislocation of ***R/L ***1/2/3/4/5th metatarsophalangeal dislocation
POST-PROCEDURE DIAGNOSIS: Same (refer above)
PROCEDURALIST: ***
ANESTHESIA:***Conscious sedation
NAME OF PROCEDURE: Closed treatment of metatarsophalangeal dislocation with manipulation
PROCEDURE IN DETAIL:
The risks and benefits of the procedure were discussed at length with the patient. Risks discussed included but were not limited to post-procedural pain, numbness, and stiffness. The risks of conscious sedation were also discussed with the patient. Following informed verbal consent after discussion of risks and benefits, the patient agreed to proceed with the procedure. A timeout was performed.
Conscious sedation was performed with all appropriate personnel in the room. The toe was grasped and gentle traction was applied in line with the deformity. The toe was felt to relocate and deformity improved. The foot was placed into a properly fitting rigid-sole postop shoe. Radiographs were obtained which demonstrated a successful reduction without associated fractures.
After completion of the procedure, the patient’s neurovascular status was within normal limits.
NUMBER OF REDUCTION ATTEMPTS: ***
COMPLICATIONS: ***
DISPOSITION:
Discharged home weight bearing as tolerated in a hard-soled shoe with follow-up with orthopaedic surgery in 1 week.
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S93.12 | Dislocation of metatarsophalangeal joint |
| S93.14 | Subluxation of metatarsophalangeal joint |
| S93.52 | Sprain of metatarsophalangeal joint |
| S93.**1A | Right great toe, initial encounter |
| 293.**2A | Left great toe, initial encounter |
| S93.**4A | Right lesser toe, initial encounter |
| S93.**5A | Left lesser toe, initial encounter |
.webp)