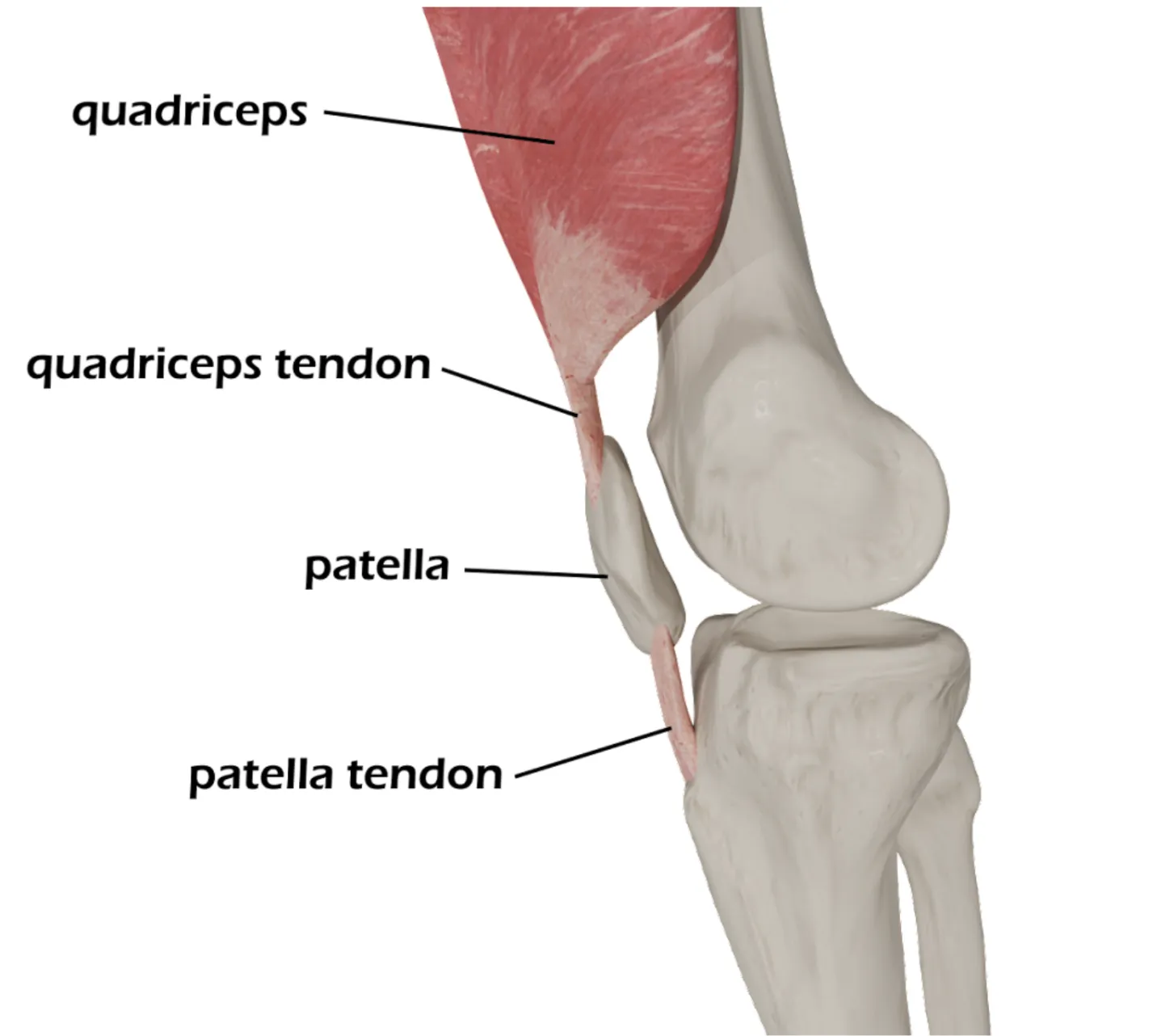
Patella / Quadriceps Tendon Rupture
- General
- Patella tendon ruptures are more likely to occur in patients <40 years old
- Quadriceps tendon ruptures are more likely to occur in patients > 40 years old
- Quadriceps tendon ruptures occur nearly twice as commonly
- Males are more commonly affected than females in both patellar and quadriceps tendon ruptures
- Immobilization & WB Status
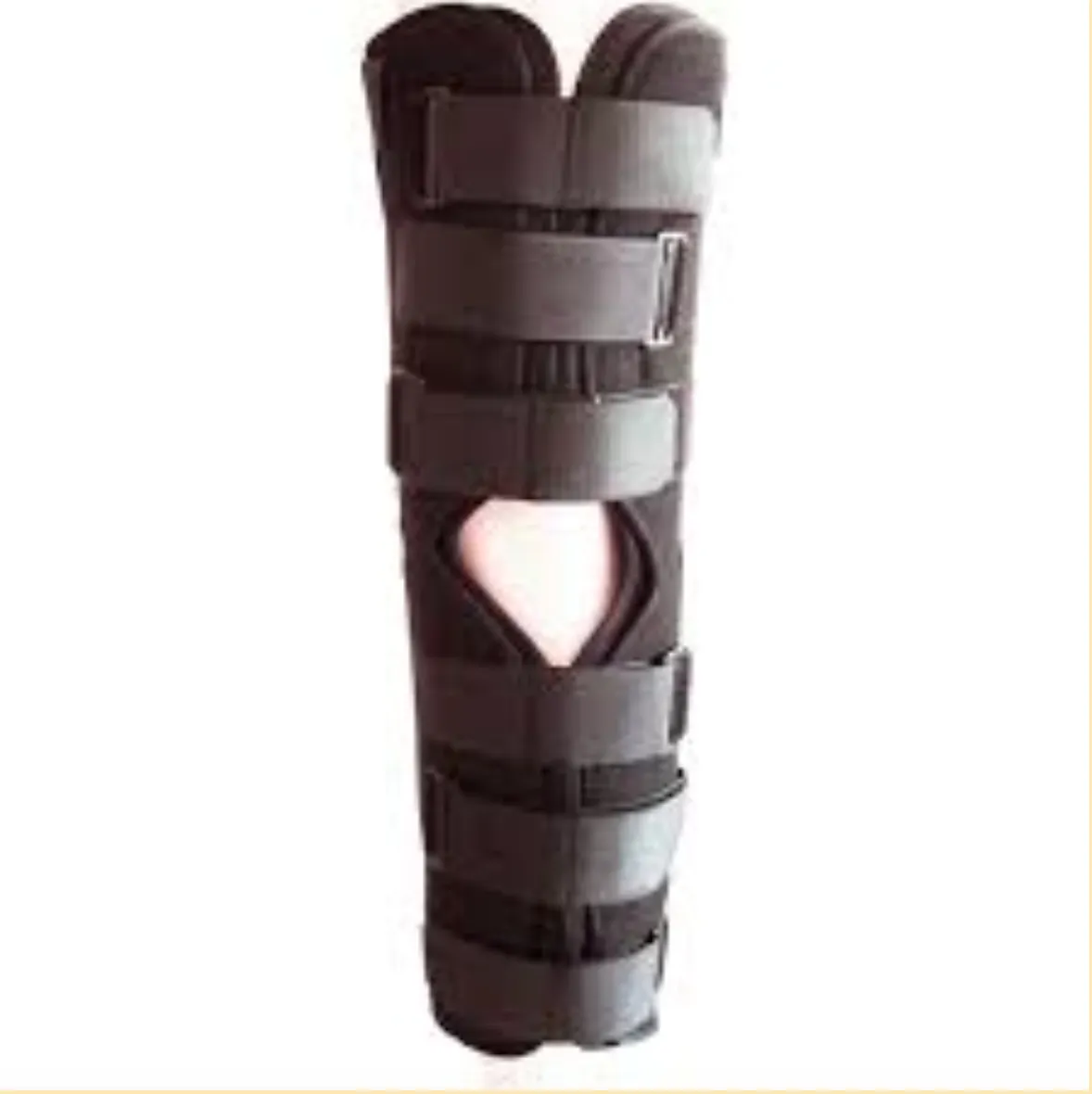
- Managed in a knee immobilizer (in full extension) with the patient allowed to weight bear as tolerated with crutches for assistance
- Disposition
- The majority of these patients can be discharged with orthopaedic followup
- Exception: complete quadriceps tendon rupture - Variations in regional practices and surgeon preferences exist for these injuries, as such contact the on-call surgeon for their preferences (e.g. formal inpatient consult vs. outpatient followup)
- Mechanism
- Quadriceps
- Eccentric quadriceps contraction
- More common: older than 40 years of age
- Patella
- Forceful quadriceps contraction with knee in flexion
- More common: younger than 40 years of age
- Timing of injury
- Other locations of pain
- General activity level
- Good to obtain for sports injuries
- Preceding pain
- May identify antecedent tendinopathy
- Comorbidities and risk factors
- Rheumatic diseases, Diabetes, SLE, connective tissue disorders, renal disease
- Weaken collagen structure and are risk factors for these types of injuries
- Chronic tendinitis
- Anabolic steroid use
- History of steroid injections
- Smoking status
Vitals
- Remove any splint or wrapping
- Effusion/swelling about the knee joint and/or locally at the injured tendon
- Palpate the quadriceps tendon and patella tendon for defect
- Quadriceps tendon is above the patella
- Patellar tendon is below the patella
- Usually will feel a palpable discontinuity in the ruptured tendon
Motor Exam:
-
Motor Exam:
- Quad/patellar tendon - Knee extension
- Limited or unable to perform secondary to quad/patellar tendon injury
- Tibialis Anterior - Dorsiflexion
- Gastroc/Soleus - Plantarflexion
- EHL/FHL - Extension/Flexion of the great toe
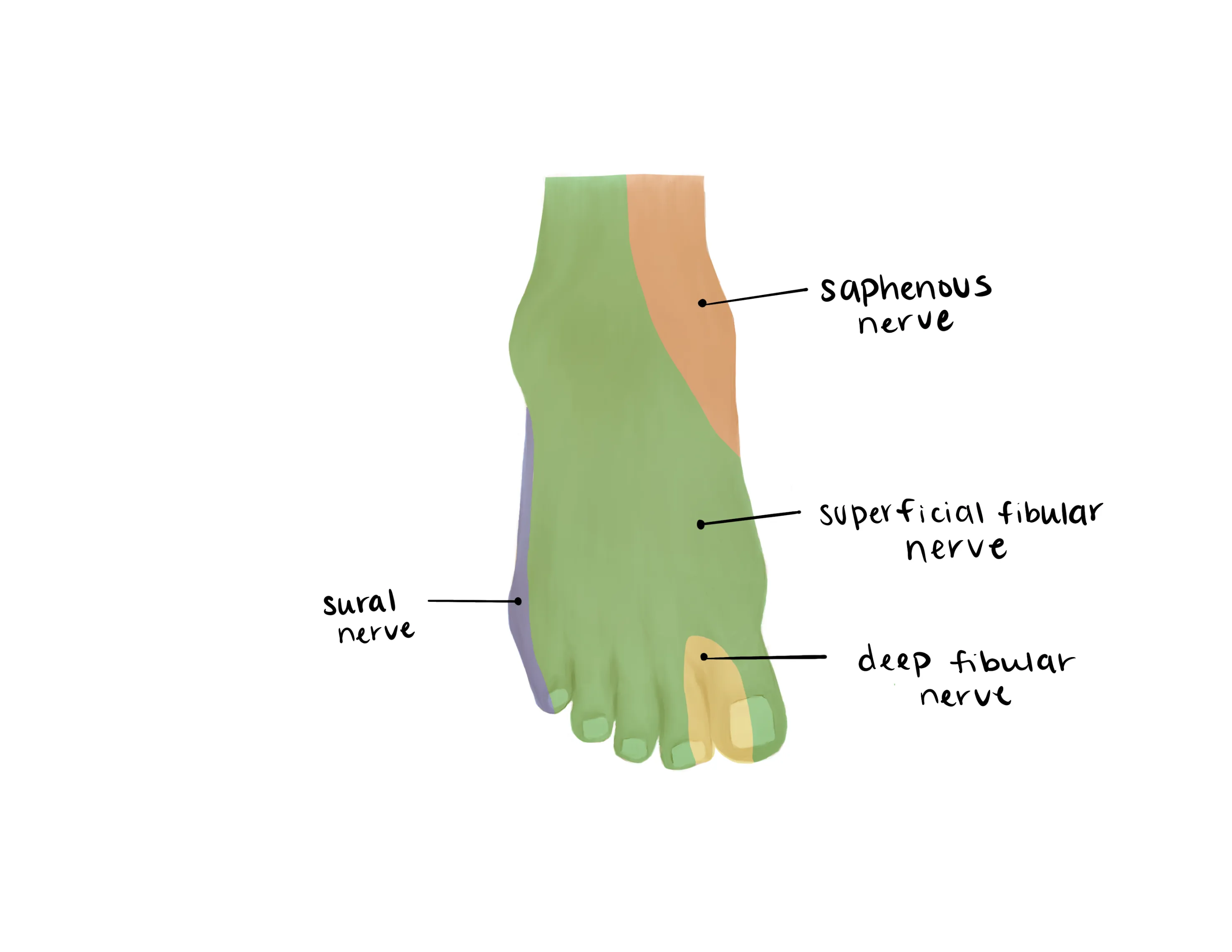
- Sural (Lateral)
- Saphenous (medial)
- Superficial Peroneal(dorsum)
- Deep Peroneal (1st web space)
- Tibial (plantar)
- Vascular Exam:
- Dorsalis Pedis/Posterior Tibial
- Capillary refill to toes
- Failure to perform straight leg raise
- Critical test to assess integrity of the extensor mechanism
- If able to actively extend the knee and maintain that position with pain but without assistance it usually indicates a partial tear
- If the patient cannot actively perform a straight leg raise but can hold the leg in extension (after being passively extended), this typically indicates the extensor retinaculum remains intact
- AP/Lateral femur, knee, tibia & fibula
- XR will show abnormal position of the patella (see below)
- Large knee effusion is often observed
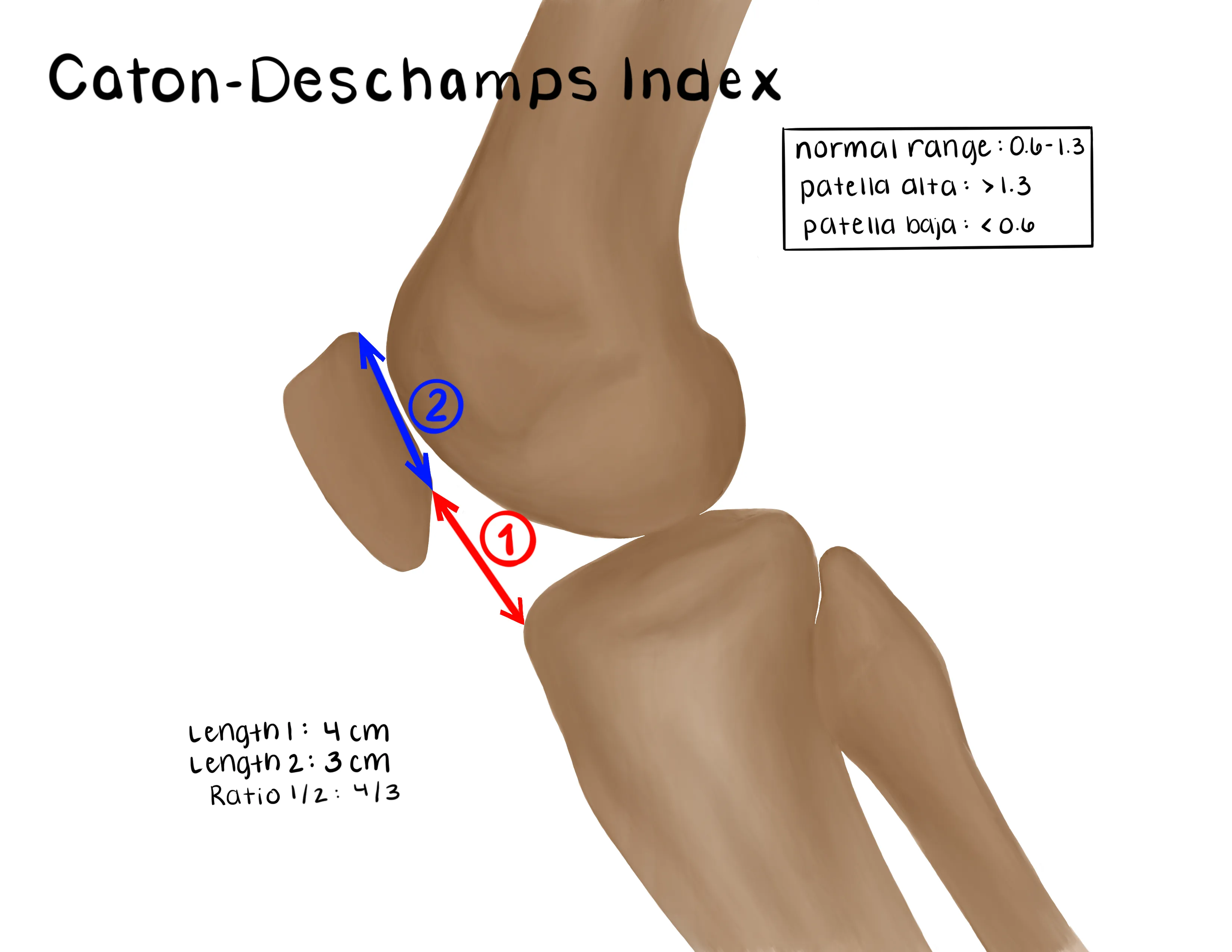
- Patella position
- Patella baja (complete quad tendon rupture)
- Patella tethered to the tibia by intact patellar tendon
- Patella alta (complete patella tendon rupture)
- Patella is detached from the tibia and tethered to the quad tendon
- Ratio to assess patellar position (multiple exist)
- Ultrasound - not required but often helpful
- Confirmatory test to visualize discontinuity of the tendon as well as effusion
- This modality is extremely user dependent but may be the fastest and least expensive option if a provider is comfortable with point-of-care ultrasound
- MRI knee - usually not required in the ED
- Can be helpful for confirming the diagnosis if equivocal findings, partial tears, or if the patellar retinaculum remains intact
- Confirmation of diagnosis and gold standard test
- Often obtained in the outpatient setting to look for other soft tissue injuries, loose bodies, etc.
Medical Decision Making
Complete Quadriceps Tendon Rupture:
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an extensor mechanism injury to the ***R/L lower extremity likely from quadriceps tendon rupture. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with inability to extend the ***R/L knee and a palpable discontinuity of the quadriceps tendon. Radiographs reveal patella baja with a knee effusion but no fractures. The on-call orthopaedist was contacted and recommended ***.
Complete Patellar Tendon Rupture:
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an extensor mechanism injury to the ***R/L lower extremity likely from patellar tendon rupture. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with inability to extend the ***R/L knee and a palpable discontinuity of the patellar tendon. Radiographs reveal patella alta with a knee effusion but no fractures. The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer and discharged with instructions to bear weight as tolerated. The patient will followup with orthopaedics within 1-2 weeks.
Partial Quadriceps Tendon Injury :
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an injury to the ***R/L lower extremity likely to have partial quadriceps tendon injury. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact. The patient is able to extend the ***R/L knee, though it is painful about the quadriceps tendon. There was no palpable discontinuity of the tendon. Radiographs reveal no fractures and no large knee effusion. The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer and permitted to bear weight as tolerated. The patient was discharged and will followup with orthopaedics within 1-2 weeks.
Partial Patellar Tendon Injury :
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of ***, who presents with an injury to the ***R/L lower extremity likely to have partial patellar tendon injury. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact. The patient is able to extend the ***R/L knee, though it is painful about the patellar tendon. There was no palpable discontinuity of the tendon. Radiographs reveal no fractures and no large knee effusion. The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer and permitted to bear weight as tolerated. The patient was discharged and will followup with orthopaedics within 1-2 weeks.
Complete quadriceps tendon rupture (differences in orthopedic practices) :
- Contact on-call orthopedist
- May recommend discharge with close follow-up to clinic vs. formal consult with admission for operative repair
- WB status: weight bearing as tolerated in knee immobilizer (full extension)
- Diet: per discussion from orthoapedics
- Analgesia: oral narcotic pain medication, acetaminophen (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Knee immobilizer with leg in full extension
- Disposition: per orthopaedist
- WB status: weight bearing as tolerated in knee immobilizer (full extension)
- Diet: regular
- Analgesia: short oral course of narcotic pain medication, acetaminophen (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Knee immobilizer with leg in full extension
- Disposition: home with follow up with orthopaedics in 1-2 weeks
- WB status: weight bearing as tolerated in knee immobilizer (full extension)
- Diet: regular
- Analgesia: short oral course of narcotic pain medication, acetaminophen (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 15 pills
- Immobilization: Knee immobilizer with leg in full extension
- Disposition: home with follow up with orthopaedics in 1-2 weeks
Materials
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S76.12 | Laceration of quadriceps muscle, fascia and tendon |
| S76.121 | Laceration of right quadriceps muscle, fascia and tendon |
| S76.122 | Laceration of quadriceps muscle, fascia and tendon |
| S76.1**A | Injury of quadriceps muscle, fascia, and tendon, initial encounter |
| S76.11*A | Strain |
| S76.12*A | Laceration |
| S76.19*A | Other specified injury |
| S76.1*1A | Right |
| S76.1*2A | Left |