Hip Fracture
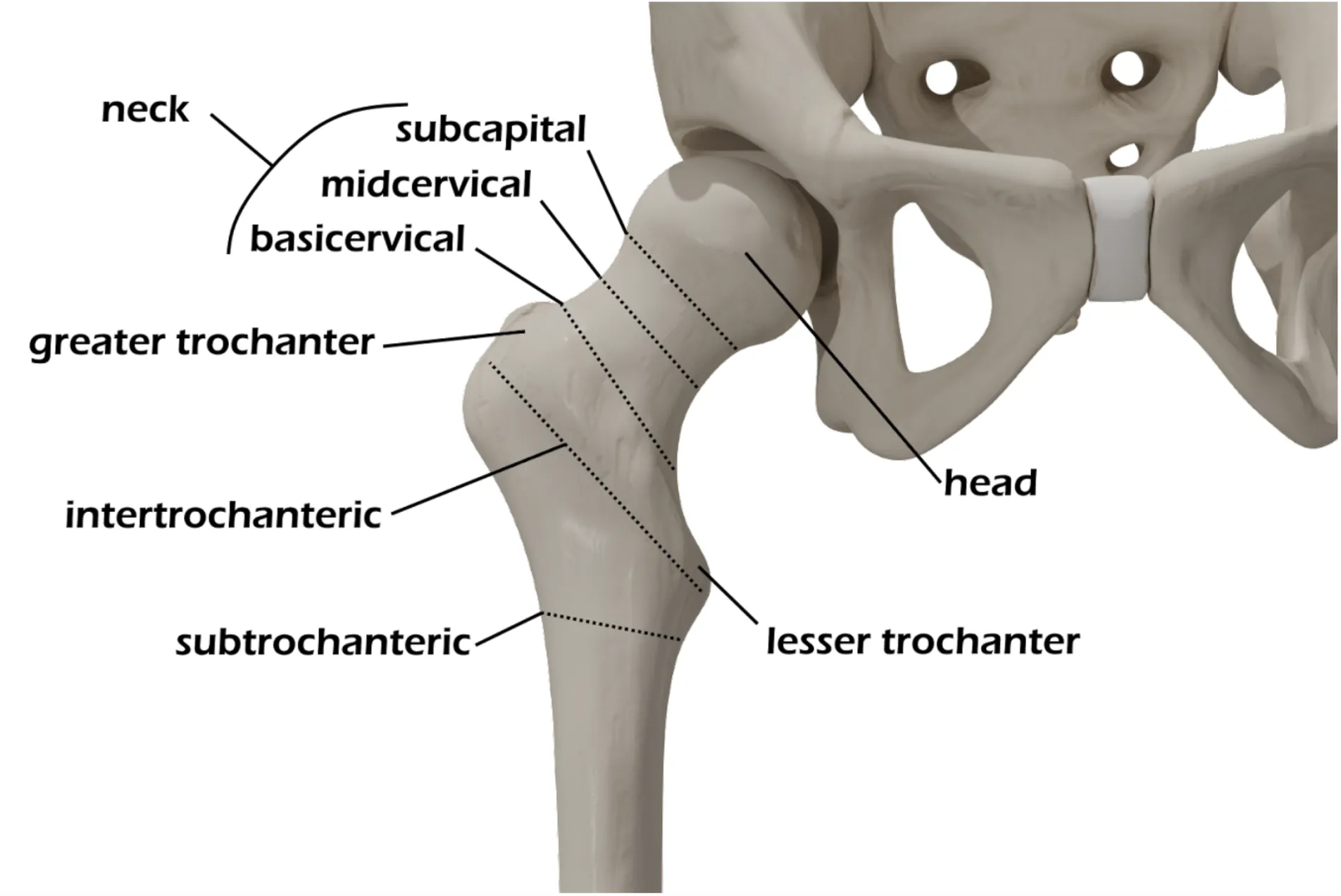
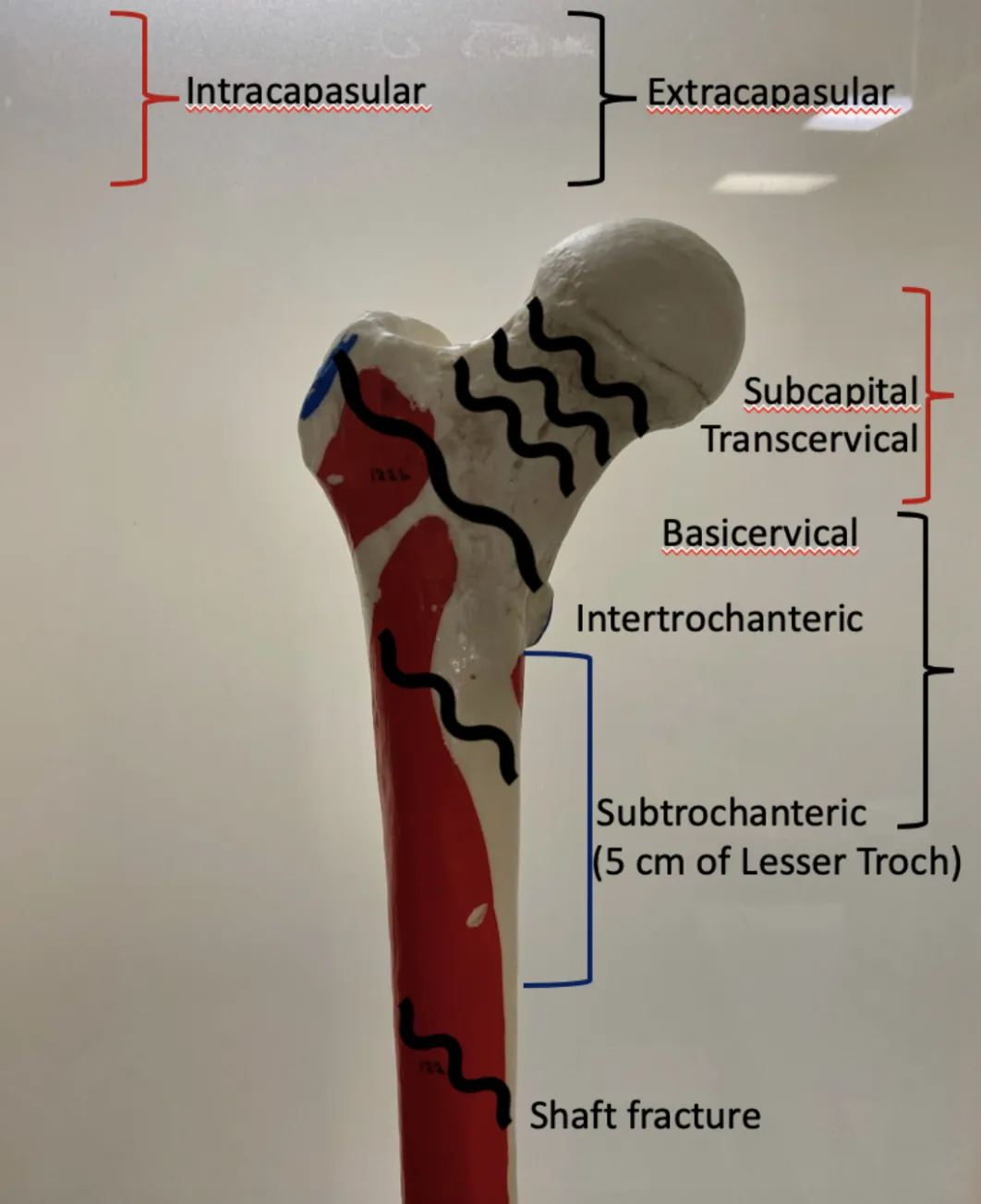
- Hip (proximal femur) fractures are generally categorized as:
- Neck (subcapital, mid/transcervical, basicervical)
- Intertrochanteric
- Subtrochanteric
- Head
- Isolated fractures of the greater or lesser trochanter may also occur, but present a different clinical picture
- Mandates an orthopaedic consult
- Patients are typically admitted for definitive (operative) treatment
- Early operative treatment (< 48 hours) has been shown to improve outcomes and mortality rates
- Mechanism
- If it is a fall, determine mechanical or syncopal
- Implications for further medicine workup and injury prevention in the future
- Common fragility fracture in the elderly
- In young, healthy patients with history of high energy trauma, consider pathologic fracture
- Timing of injury
- Goal is to perform hip fracture surgery within 48 hours
- Improved outcomes and decreased mortality
- Other locations of pain
- Distracting injury
- Other fragility fractures may be present
- Numbness or tingling
- Antecedent hip pain
- Especially if low energy mechanism - consider and look for pathologic fracture
- Baseline ambulation (assistive device? Community vs home ambulator?)
- Functional status has implication on total hip arthroplasty vs. hemiarthroplasty
- Healthy, high functioning = THA (generally)
- Sick, low functioning = Hemiarthroplasty (generally)
- Knowledge of baseline ambulation will help set realistic postoperative goals
- Comorbidities: heart disease, diabetes, lung disease, smoking, etc.
- Anticoagulation
- Timing of last dose
- Last time patient last ate (NPO status)
Vitals
- Resting position of the injured lower extremity
- Most commonly shortened and externally rotated
- Assess skin - bruising, swelling, ecchymosis
- Pain with logroll
- Palpate remainder of the extremity to assess for ipsilateral injuries
Motor Exam:
-
Motor Exam:
- Tibialis Anterior - Dorsiflexion
- Gastroc/Soleus - Plantar flexion
- EHL/FHL - Extension/Flexion of the great toe
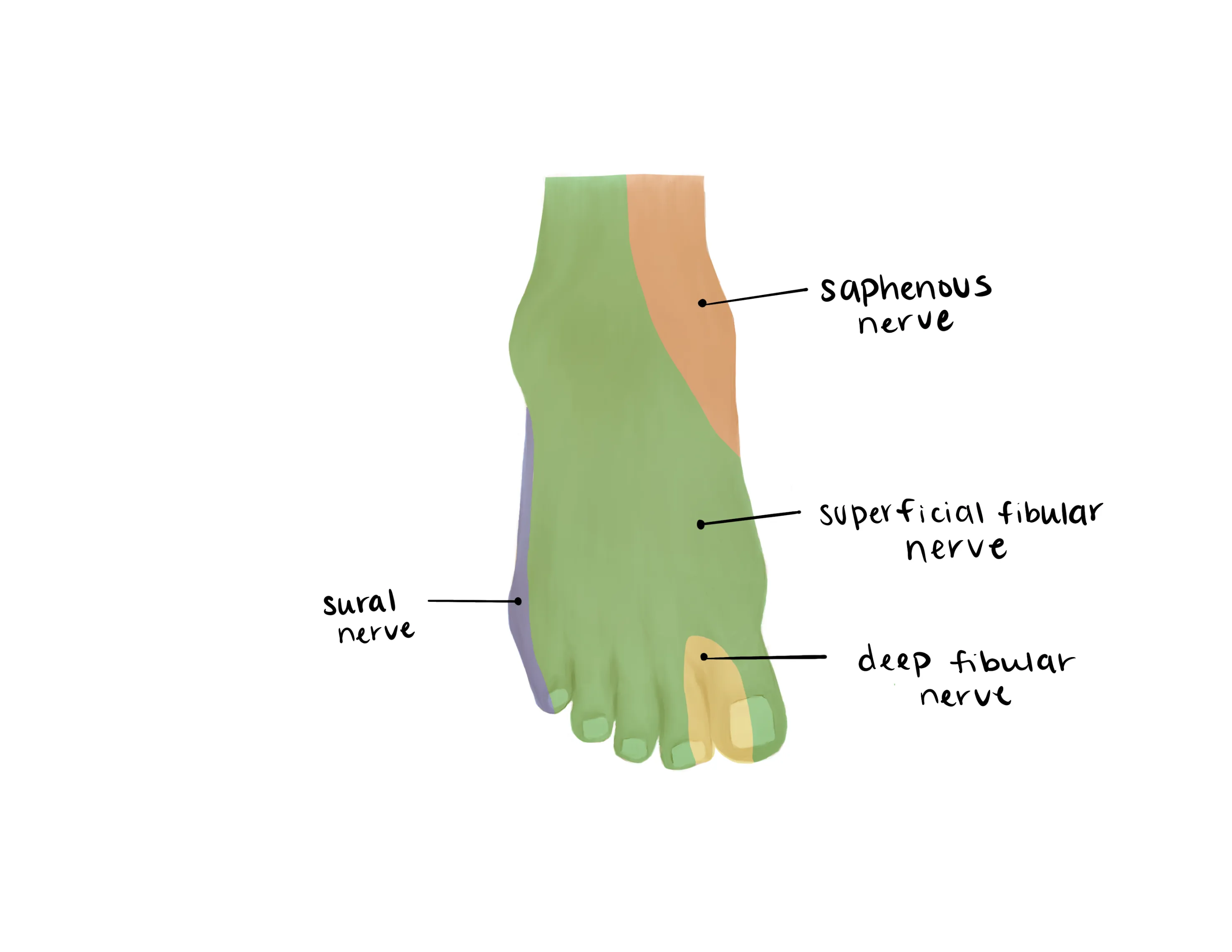
- Sural (Lateral)
- Saphenous (medial)
- Superficial Peroneal(dorsum)
- Deep Peroneal (1st web space)
- Tibial (plantar)
- Vascular Exam:
- Dorsalis Pedis/Posterior Tibial
- Capillary refill to toes
- Motion at the hip and knee limited secondary to pain
Medical Decision Making
Hip fracture (femoral neck fx, intertrochanteric fx, subtrochanteric fx) :
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of *** who presents with an injury to the ***R/L hip which occurred while mechanism***, found to have a ***femoral neck/intertroch/subtroch fracture. The patient denies antecedent pain but uses a ***cane/walker for assistance with ambulation. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with pain on logroll and a shortened, externally rotated ***R/L lower extremity. Radiographs reveal ***. Orthopaedics and internal medicine were consulted. The patient was made npo and last ate ***.
Hip fracture:
- Consult Orthopaedic Surgery & Internal Medicine
- WB status: Non-weight-bearing injured lower extremity
- Diet: NPO
- Labs: Type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP
- Analgesia: oral analgesia with IV narcotic for breakthrough
- Ex: 5-10mg oxycodone q4, 0.5mg hydromorphone q4 prn, tylenol 975mg q8hr scheduled
- At some institutions, regional blocks can be placed in the ED for pain control. If this is a capacity of your institution, notify anesthesia who would perform this.
- Immobilization: None
- Disposition: Admission to internal medicine
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S72.0 | Fracture of head and neck of femur |
| S72.02 | Fracture of epiphysis (separation) (upper) of femur |
| S72.03 | Midcervical fracture of femur |
| S72.04 | Fracture of base of neck of femur |
| S72.06 | Articular fracture of head of femur |
| S72.11 | Fracture of greater trochanter of femur |
| S72.12 | Fracture of lesser trochanter of femur |
| S72.14 | Intertrochanteric fracture of femur |