Distal Femur Fracture
- Distal femur fractures often result from high energy injuries in younger patients, but may result from low energy mechanisms (e.g. mechanical fall) in the elderly
- Patients generally require admission
- Indications for immediate orthopedic consultation include:
- Open fracture
- Associated knee dislocation
- Mechanism
- Elderly - often low-energy mechanisms (e.g. fall from standing height)
- Younger patients - high-energy axial loading with additional varus, valgus, or rotational force
- Timing of injury
- Other locations of pain
- Often a distracting injury, resulting in neglecting concurrent injuries
- Ensure you palpate the remained of the extremities, chest, pelvis, spine on exam to decrease the risk of missed injuries
- Numbness or tingling
- Comorbidities
- Heart disease, diabetes, lung disease, smoking
- Anticoagulation
- Time of last dose
- Last time patient last ate (NPO status)
Vitals
- Remove any splint/wrapping to view the distal femur
- Basic appearance of leg (swelling, bruising)
- Assess for poke hole/punctate wounds → open fracture
- Do not miss this and confirm antibiotics were given
- Pain with logroll of the extremity
- Palpate the compartments (anterior, posterior, adductor) in the leg
- Good to establish baseline, as subsequent bleeding and edema can develop into compartment syndrome after presentation
- Lower risk than lower leg due to increased soft tissue space
- Palpate remainder of the extremity to assess for ipsilateral injuries
Motor Exam:
-
Motor Exam:
- Tibialis Anterior - Dorsiflexion
- Gastroc/Soleus - Plantar flexion
- EHL/FHL - Extension/Flexion of the great toe
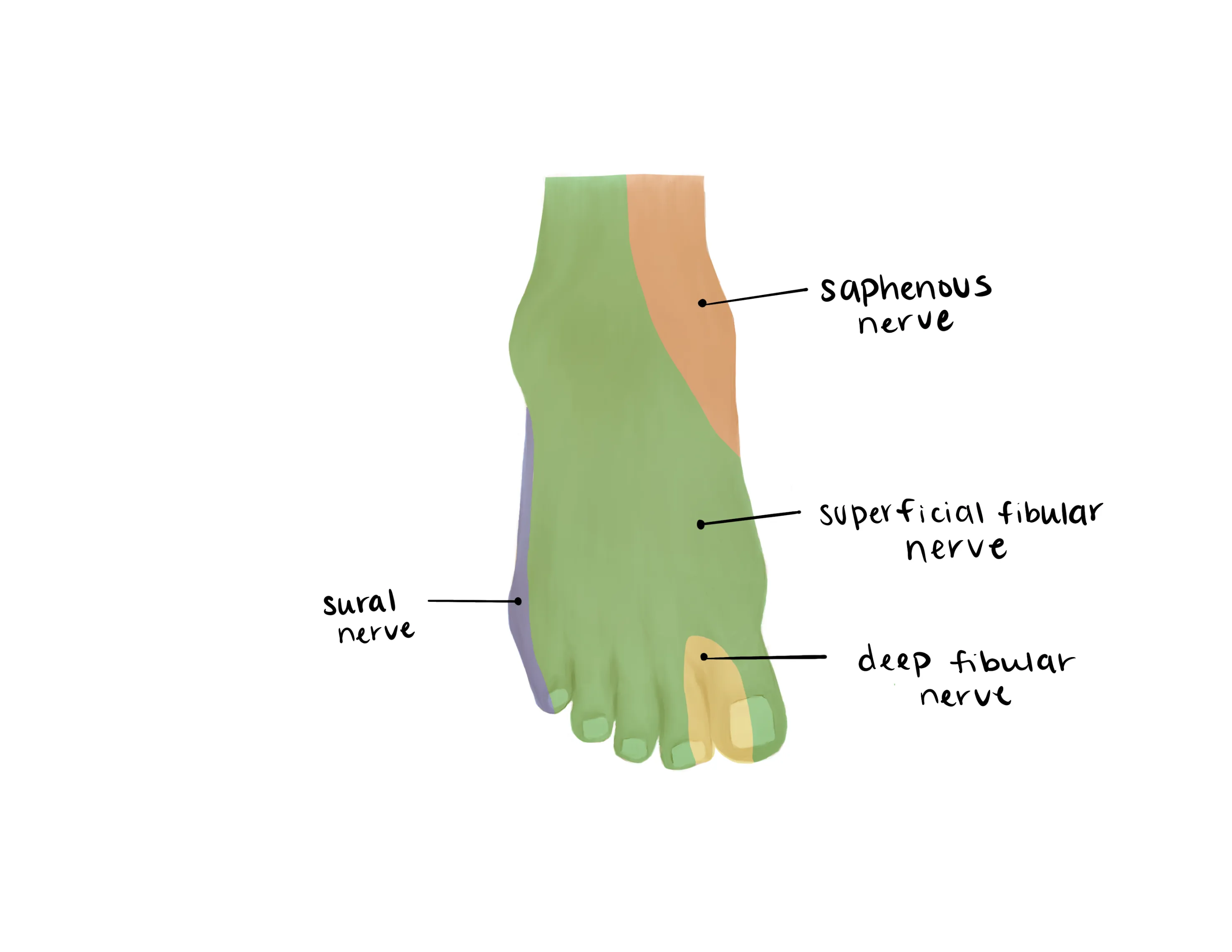
- Sural (Lateral)
- Saphenous (medial)
- Superficial Peroneal(dorsum)
- Deep Peroneal (1st web space)
- Tibial (plantar)
- Vascular Exam:
- Dorsalis Pedis/Posterior Tibial
- Capillary refill to toes
- Motion at the hip and knee limited secondary to pain
- AP/Lateral ipsilateral hip, AP/Lateral femur, AP/Lateral knee
- CT of the distal femur/knee
- Often helpful but this to leave to the discretion of orthopaedics
- Recommended if concerned for intraarticular extension
- Recommended for severe comminution
Medical Decision Making
Closed distal femur fracture :
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of *** who presents with an injury to the ***R/L lower extremity which occurred while mechanism***, found to have a closed distal femur fracture. Associated injuries include ***. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with pain on logroll. The injury was closed without any poke holes or punctate wounds that probe deep. Radiographs reveal ***. The injured extremity was placed in a knee immobilizer and orthopaedics was consulted.
Open distal femur fracture fracture :
*** is a *** y/o ***M/F with hx of *** who presents with an injury to the ***R/L lower extremity which occurred while mechanism***, found to have an open distal femur fracture. Associated injuries include ***. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with a laceration on the *** side of the distal thigh that probed deep. The patient was given an immediate dose of IV ancef/gentamicin***. The laceration was irrigated at bedside of gross contaminants. Orthopaedics was consulted and the patient was made NPO. Radiographs reveal ***. Orthopaedic surgery to admit the patient and assume care.
Closed distal femur fracture:
- Consult Orthopaedic Surgery
- WB status: Nonweightbearing injured lower extremity
- Diet: NPO
- Labs: ABG, Lactate (for high energy mechanism and polytrauma)
- Used to assess operative timing
- Analgesia: oral analgesia with IV narcotic for breakthrough
- Ex: 5-10mg oxycodone q4, 0.5mg hydromorphone q4 prn, tylenol 975mg q8hr scheduled
- Immobilization: knee immobilizer
- Disposition: Likely admission to orthopaedics versus general surgery trauma
- If polytraumized patient often admitted to general surgery trauma
- Consult Orthopaedic Surgery
- Ensure IV antibiotics were given (ancef vs. gentamicin)
- Gustillo-Anderson chart for antibiotic type and dose
- Diet: NPO preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- Labs: ABG, Lactate (for high energy mechanism and polytrauma)
- Used to assess operative timing
- Immobilization: knee immobilizer
- Disposition: Admission to orthopaedics versus general surgery trauma
- If polytraumized patient often admitted to general surgery trauma
Materials
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S72.4 | Fracture of lower end of femur |
| S72.42 | Fracture of lateral condyle of femur |
| S72.43 | Fracture of medial condyle of femur |
| S72.44 | Fracture of lower epiphysis (separation) of femur |
| S72.45 | Supracondylar fracture without intracondylar extension of lower end of femur |
| S72.46 | Supracondylar fracture with intracondylar extension of lower end of femur |