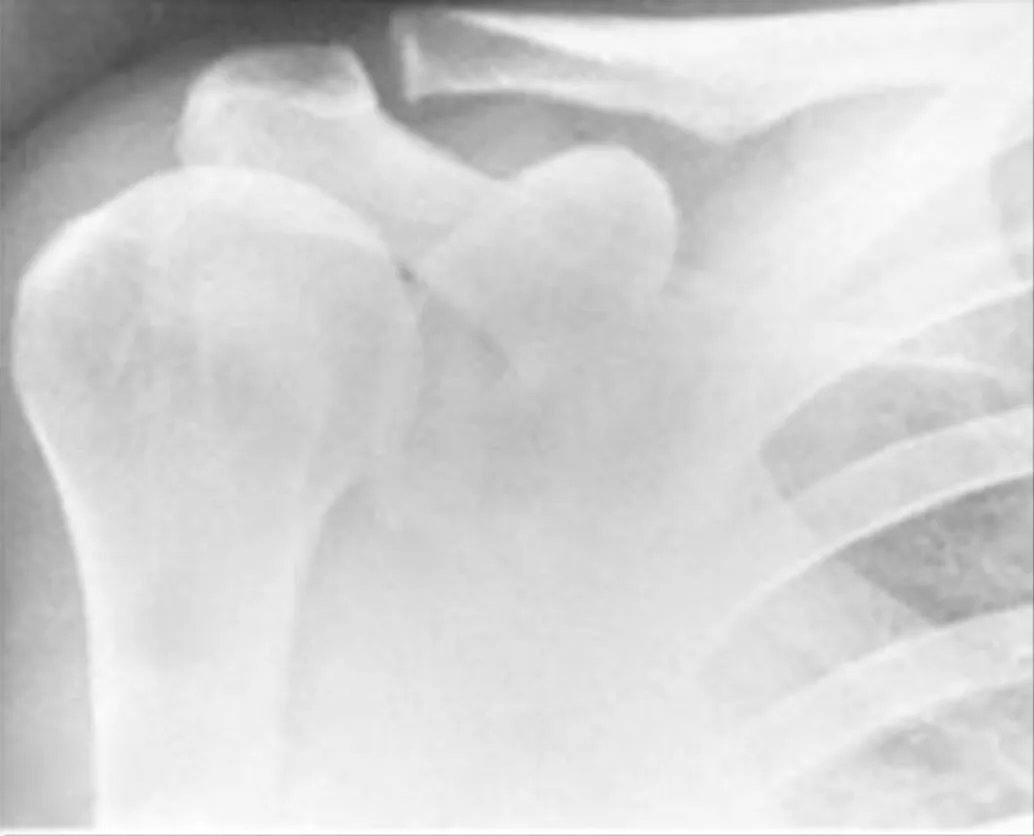
Acromioclavicular Separation
- Mechanism
- Direct blow such as a fall onto an adducted shoulder is most common
- Common athletic injury (e.g. football, snowboarding, etc.)
- Timing of injury
- Acute vs. chronic
- Other locations of pain
- Must rule out injuries to the head and neck
- Rule out associated fractures (e.g. clavicle, humerus, etc.)
- Numbness or tingling?
- Severe injury can injure brachial plexus
- Hand dominance (right vs. left hand dominant)
- Profession
- Sporting involvement
- Often occurs in athletes (high level versus recreational athlete)
Vitals
- Deformity - abnormal contour of the shoulder compared to contralateral side
- Threatened skin (tented and blanched skin) or open injury (traumatic arthrotomy)
- If traumatic arthrotomy, ensure 2-3g of IV cefazolin (Ancef) given, consult to orthopaedic surgery
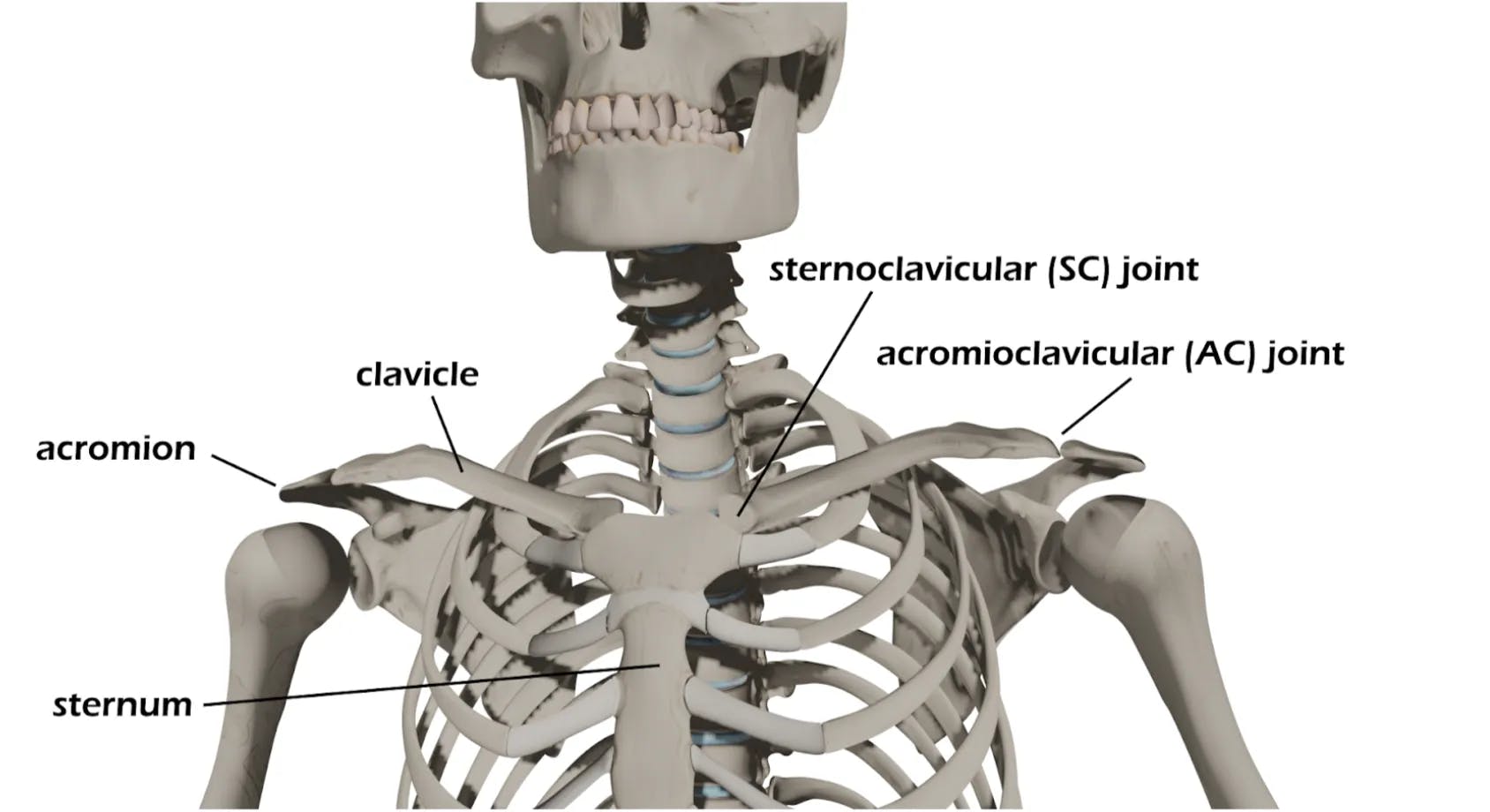
- Tender to palpation over the AC joint
- Palpate the remainder of the upper extremity and clavicle to assess for other injury
Motor Exam:
- Axillary nerve
- Assess function by getting the patient to push elbow posteriorly into the gurney
- Typical abduction of the shoulder is difficult to assess secondary to pain
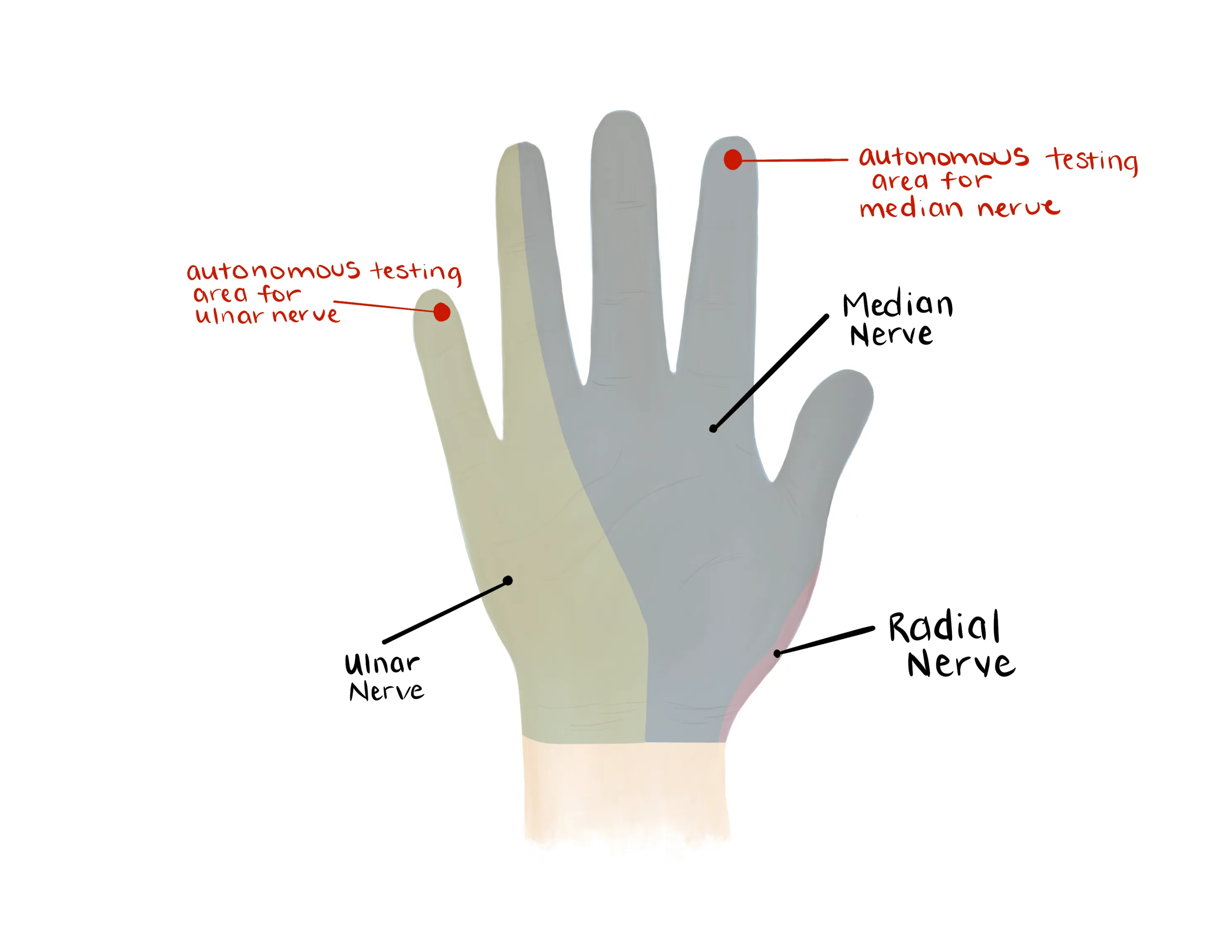
- Median Nerve/ Anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)
- Opposition of the thumb
- Opponens innervated by the median nerve - helpful to assess if concern for acute carpal tunnel syndrome
- Flexion of wrist, fingers, thumb
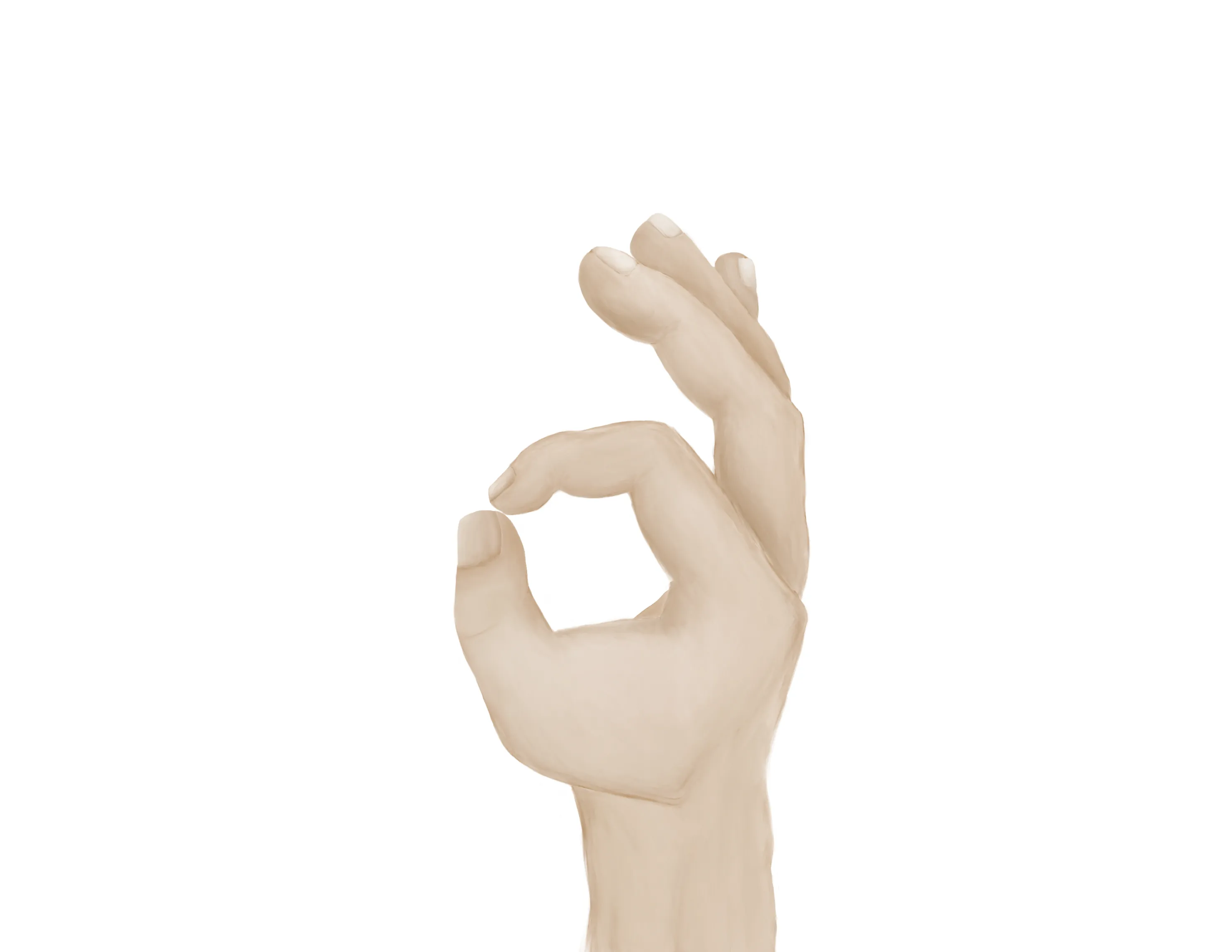
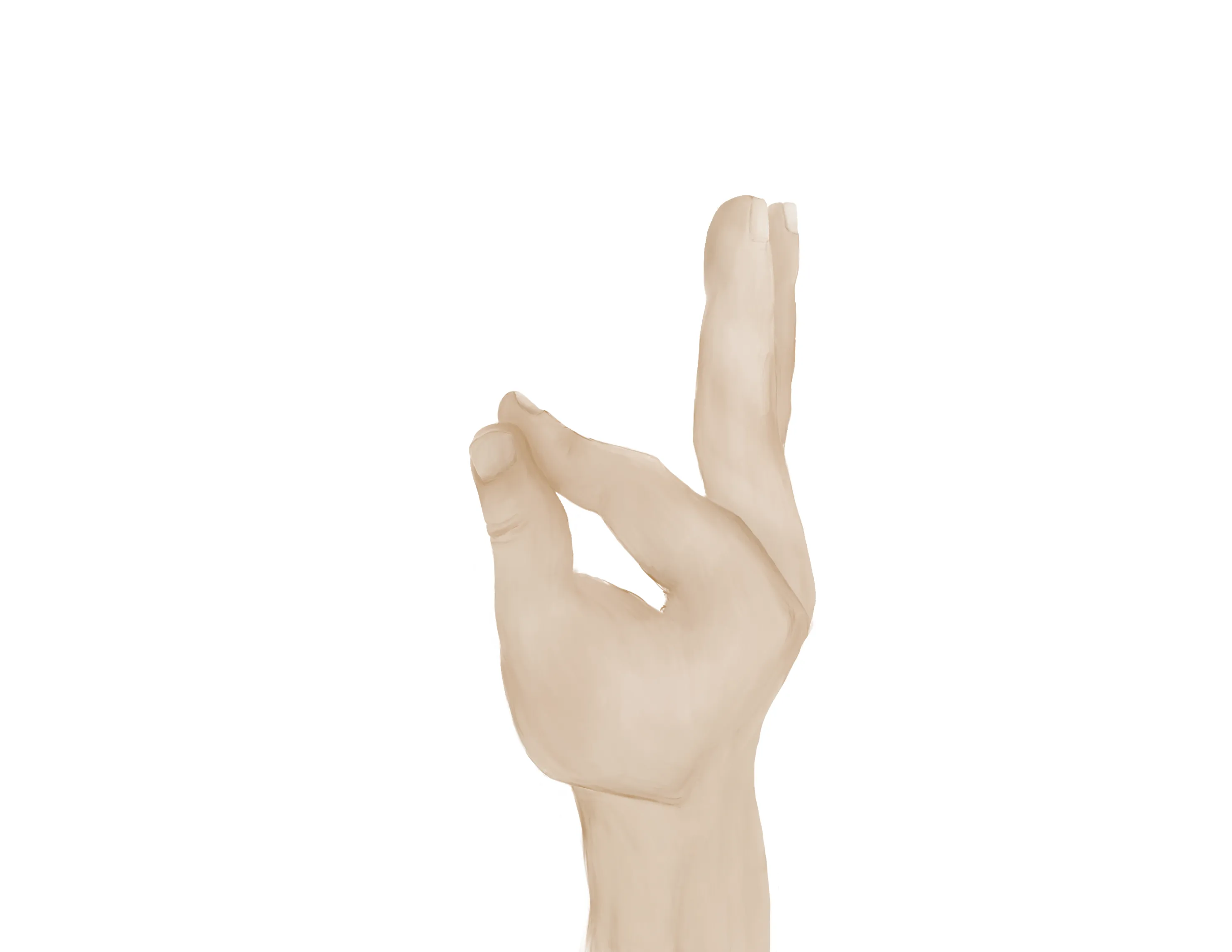
- “A-OK sign” = AIN
- Tests flexion of thumb IP joint (FPL) and flexion of index DIP joint (FDP)
- Radial nerve/ Posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)
-

- Extension of wrist, fingers, thumb
- Radial nerve palsy is common seen in humeral shaft fractures especially midshaft and distal third
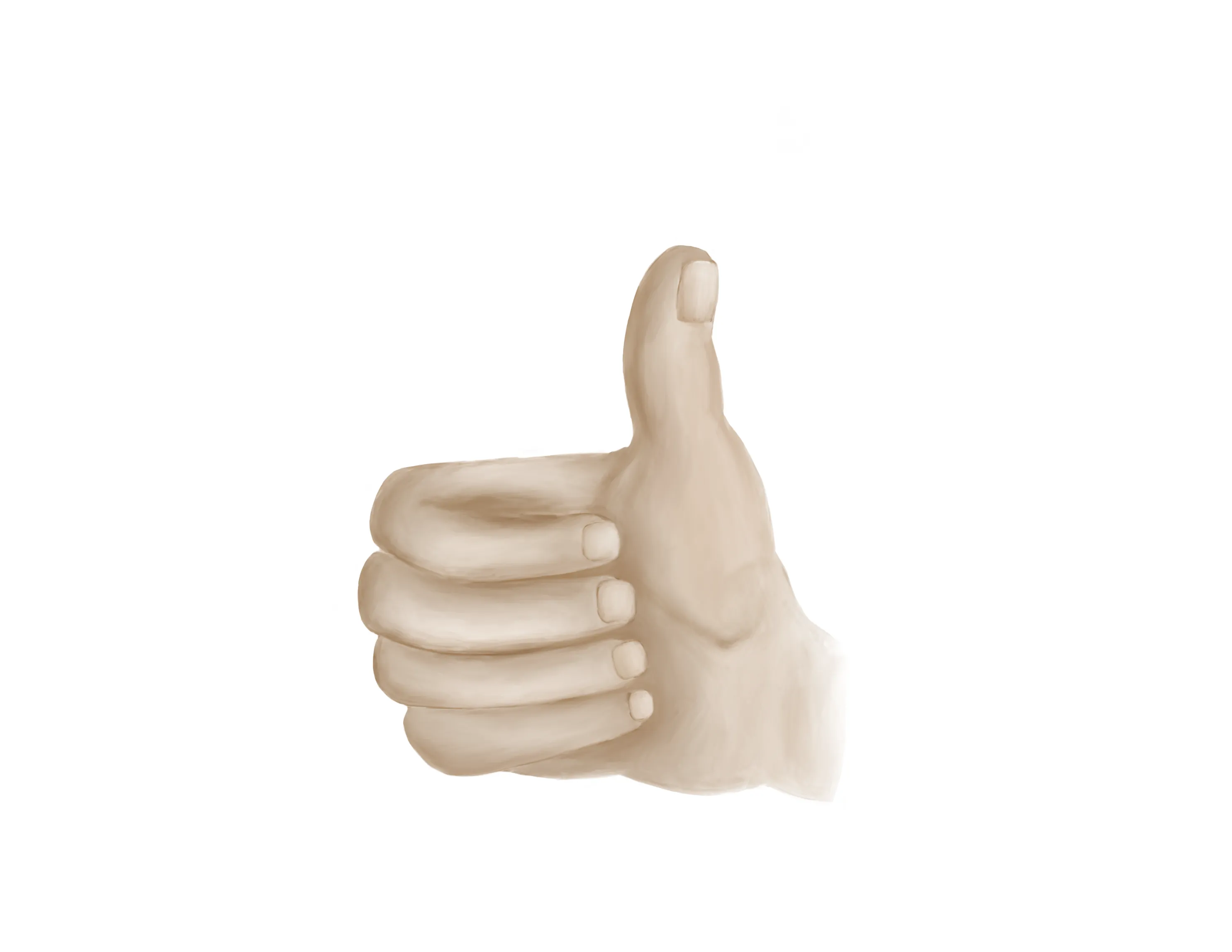
- “Thumbs up” = PIN
- Tests extension of thumb IP and MCP joints (EPL))
- Palm on flat surface and lifting/extending thumb off the surface is also a good test for PIN (tests extension of thumb MCP joint (EPL))
- Ulnar nerve
- Median, Radial, Ulnar nerve distributions
- Radial artery, Ulnar artery
- If having difficulty with palpation of radial artery, find a US doppler
- Capillary refill to digits
- Likely limited ROM about the shoulder secondary to pain
- AP/Scapular Y/axillary lateral vs. velpeau shoulder, Zanca view
- Can obtain radiographs of contralateral side for comparison if needed
- Axillary lateral view - confirm shoulder is in concentric alignment
- Axillary lateral vs. Velpeau of shoulder
- Important to rule out concomitant shoulder dislocation which may not always be apparent on AP
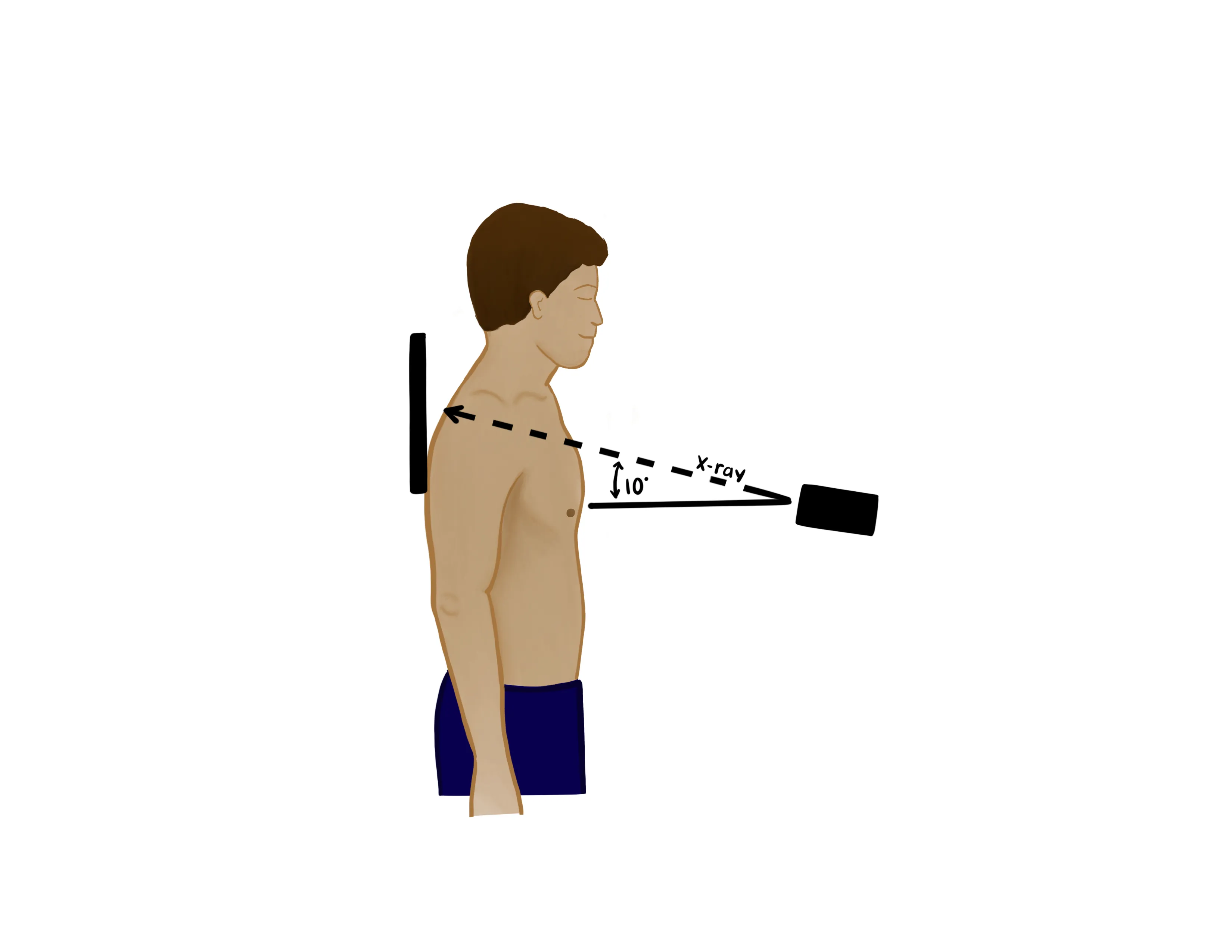
- Zanca view
- Is a special view to look down the plane of the AC joint with minimal superimposition of bony structure which may obscure more traditional views
- Performed by tilting the XR beam 10-15 degrees cephalad
Medical Decision Making
Closed AC Separation without Tenting Skin :
*** is a *** y/o ***R/L hand-dominant individual with a history of *** presenting with an injury to the *** shoulder which occurred while ***, found to have a closed AC separation. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with no poke holes or punctate wounds or tenting skin. There is tenderness to palpation and localized edema about AC joint. Radiographs reveal ***. The patient was placed in a sling and will follow up with orthopaedic surgery within 7-10 days.
Open or Tenting AC Separation :
*** is a *** y/o ***R/L hand-dominant individual with a history of *** presenting with an injury to the *** shoulder which occurred while ***, found to have an open/tenting*** AC separation. On exam, the patient is neurovascularly intact with an open wound/tenting skin*** about the AC joint. The patient was given ***ancef/gentamicin immediately after identifying the open injury. Radiographs reveal ***. Orthopaedics was consulted and will provide further recommendations. The patient is npo and last ate ***.
If open injury:
- Consult orthopaedic surgery immediately
- NPO, preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- Ensure IV antibiotics were given (ancef, gentamicin)
- Gustillo-Anderson chart for antibiotic type and dose
- Consult orthopaedic surgery immediately
- NPO, preop labs (type and screen, INR, aPTT, CBC, BMP)
- WB status: Nonweightbearing injured upper extremity, remain in sling
- Diet: Regular
- Analgesia: short course of narcotic pain medication, tylenol (scheduled)
- Ex: 5mg oxycodone q4 - 25 pills
- Immobilization
- Sling immobilization
- Disposition: Home with follow up in orthopedic surgery clinic in 1 week
| Common ICD-10 Codes | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| S43.11 | Subluxation of acromioclavicular joint |
| S43.12 | Dislocation of acromioclavicular joint, 100%-200% displacement |
| S43.13 | Dislocation of acromioclavicular joint, greater than 200% displacement |
| S43.14 | Inferior dislocation of acromioclavicular joint |
| S43.15 | Posterior dislocation of acromioclavicular joint |
| S43.16 |